What you need to know about vein valves
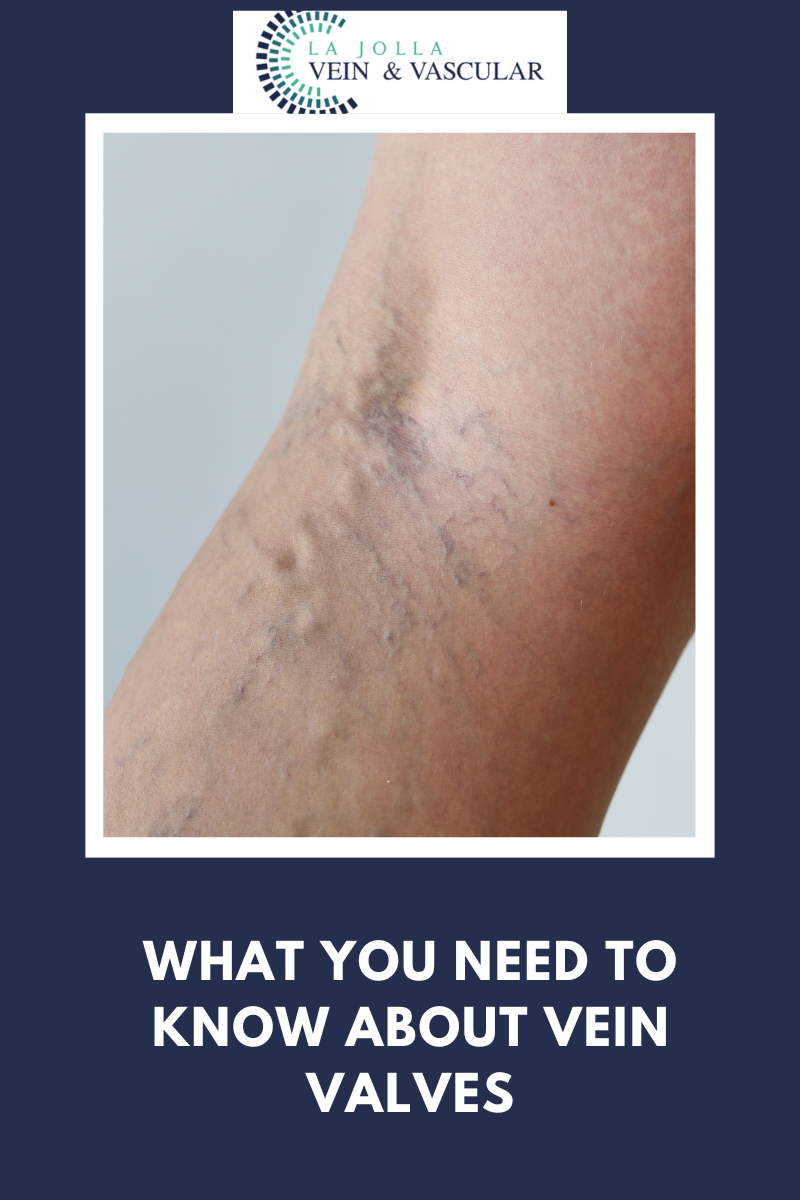
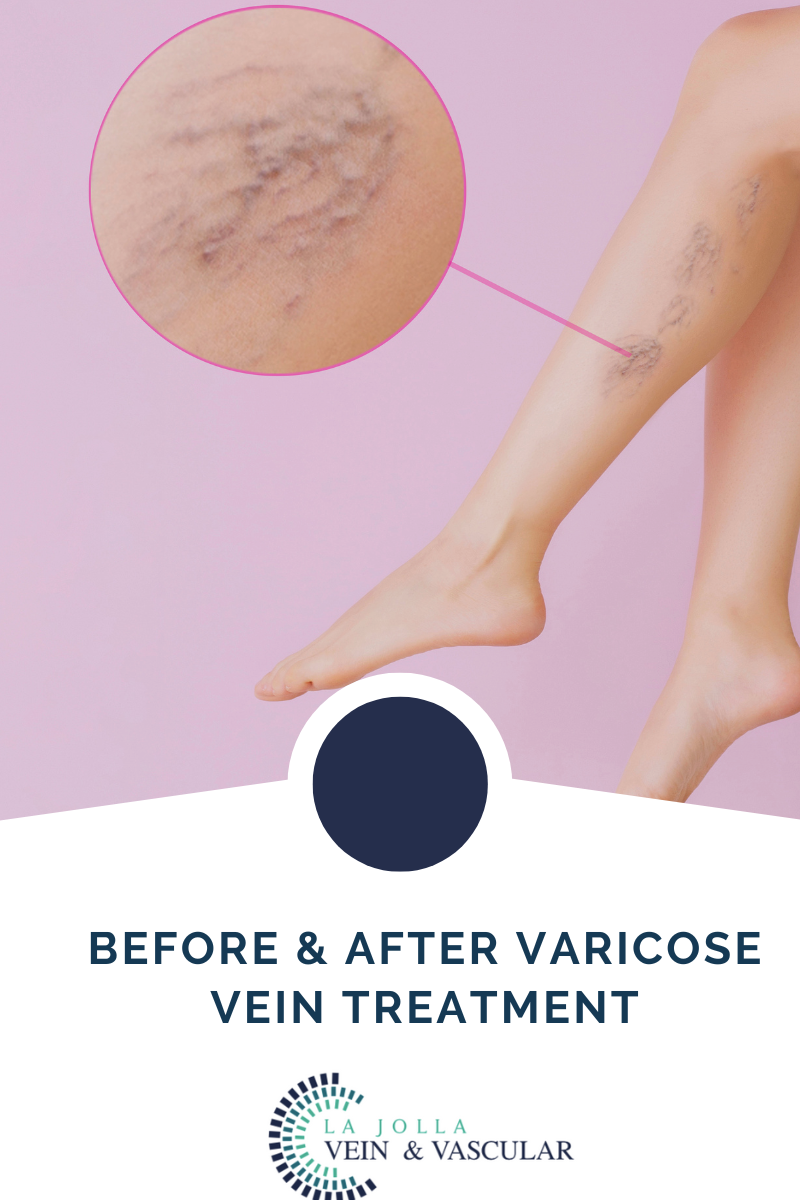
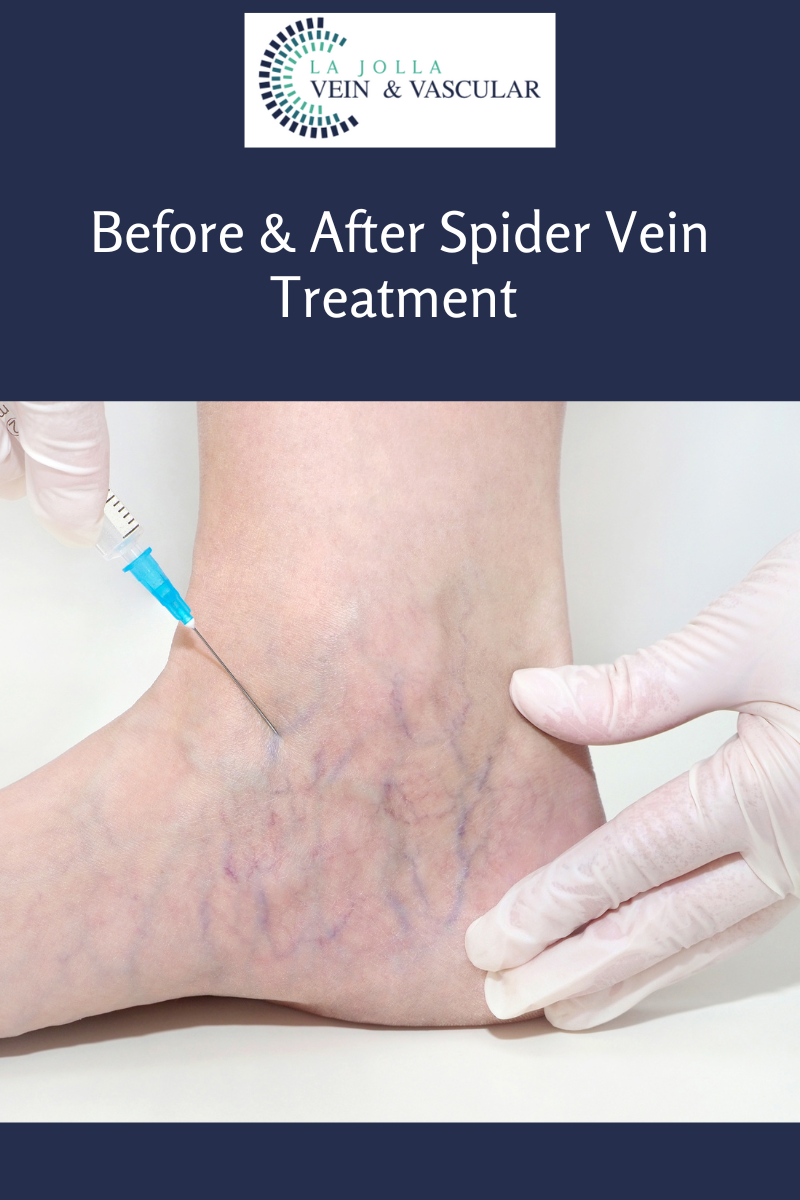
LJVascular2022-07-20T15:40:53-07:00In the circulatory system, the vein valves carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. The leg veins carry blood toward the heart, against gravity. Therefore, the leg veins have one-way valves to prevent backflow of blood. When the valves do not function properly, they allow blood to flow backward, causing the pooling of […]