What is Venous Reflux Disease?
What is Venous Reflux Disease?
Venous reflux disease is also known as venous stasis, venous insufficiency or venous incompetence and refers to ‘leaky valves’ in the veins of the legs.
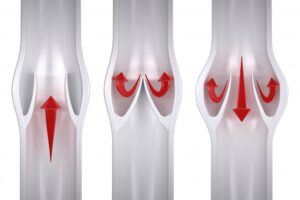
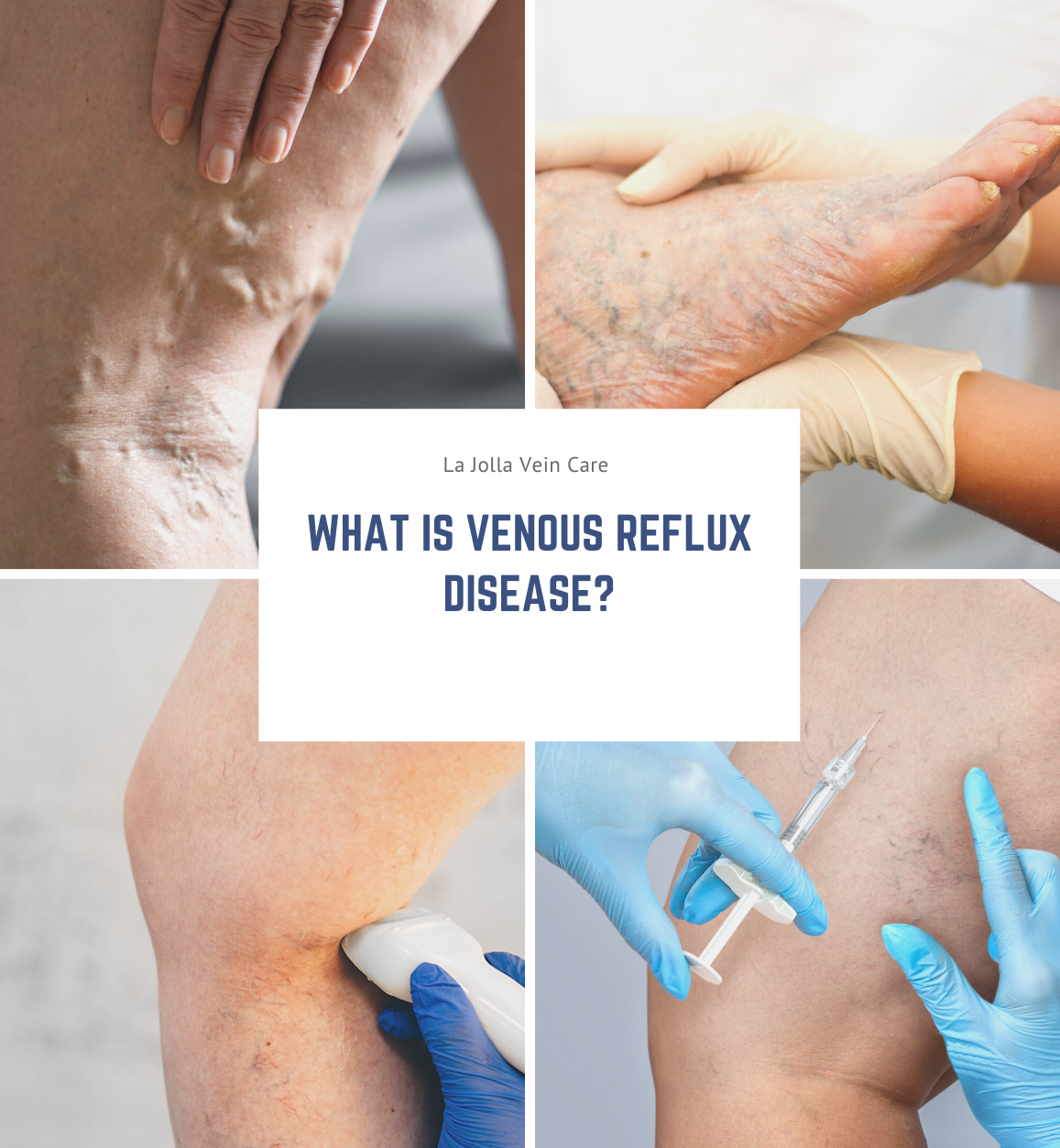
Reflux may occur in the deep and/or superficial leg veins. The deep veins are those within the muscle; they bring at least 80-90% of the blood from the legs back to the heart. The superficial veins are outside the muscle and under the skin. The main superficial veins are the Great Saphenous Vein that courses up the middle of the thigh and calf and small saphenous vein. Normally, there are one-way valves within the leg veins, which help blood flow in one direction: toward the heart. This means blood is traveling against gravity. The calf muscle also helps move blood toward the heart. When vein valves are leaky, blood flows backward (reflux) towards the feet. Blood pools in the lower legs, causing bulging veins at the surface.
Symptoms of Venous Reflux Disease:
Symptoms of venous reflux disease include; leg heaviness, leg fatigue, leg pain, ankle swelling, phlebitis (inflamed and painful veins), restless legs at night, and night cramps. Venous reflux disease is progressive and worsens over time. Skin changes may also develop, including darkening of the skin around the ankles. The darkening of the skin is sometimes referred to as venous stasis skin changes. The skin can become dry and itchy (venous eczema). Eventually, the skin can break down causing a wound, called a venous leg ulcer. All of which are possible symptoms of venous reflux disease to look out for.
What influences the development of Venous Reflux Disease?
A patient is more likely to develop venous reflux disease if they are:
- Overweight
- Pregnant
- Have a family history of vein disease
- Have damage to the leg due to injury, surgery, or previous blood clots
- High blood pressure
- Lack of exercise
- Smoking
- A blood clot in a deep vein (calf or thigh) “deep vein thrombosis”
- Swelling and inflammation of a vein close to the skin, known as “phlebitis”
How is Venous Reflux Disease Diagnosed?
In addition to physical exam findings and medical history, an ultrasound examination is an important tool in the assessment of venous disease. Not all venous disease is visible to the naked eye, and it usually arises from veins that are beneath the surface of the skin, only visible by ultrasound technology.
The ultrasound allows us to see if the valves are leaky; it can detect the direction of blood flow and also detects blockages in the veins, for example from blood clots or scars within the veins from previous clots. The ultrasound will determine exactly which veins are “bad” or incompetent. Reflux may be detected in the deep veins (within the muscle), the great and small saphenous veins, and /or branches of the saphenous veins. This will help determine the treatment plan.