Understanding Venous Stasis Dermatitis
Understanding Venous Stasis Dermatitis
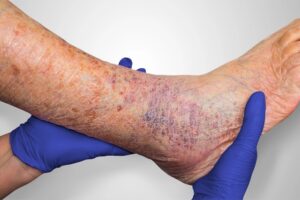
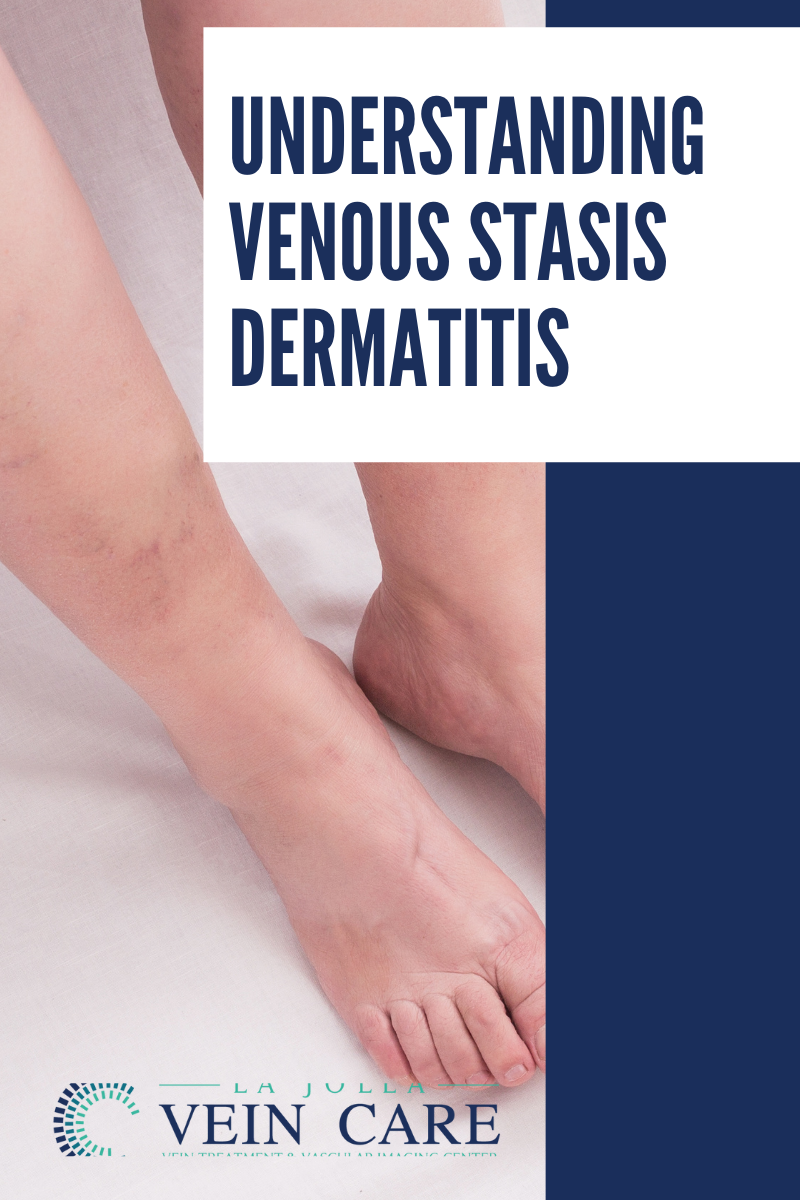
Venous stasis dermatitis is a change in the skin that occur when blood collects (pools) in the veins of the lower leg. ‘Stasis’ refers to pooling of the blood in the lower legs from venous insufficiency, and ‘dermatitis’ refers to the inflammation and related skin changes. Because of the inflammation, the skin around the ankles is usually itchy and discolored.
In venous stasis dermatitis, the skin of the ankles and lower legs may look thin or tissue-like. You may slowly get brown stains on the skin.The skin may become irritated or crack if you scratch it. It may also become red or swollen, crusted, or weepy.Over time, some skin changes become permanent. Thickening and hardening of the skin on the legs and ankles (lipodermatosclerosis)
Here’s what to look out for:
- A bumpy or cobblestone appearance of the skin
- Dark brown color
Venous stasis can cause skin sores (ulcers) may develop (called a venous ulcer or stasis ulcer). These most often form on the inside of the ankle. For this reason, skin changes are noticed around the ankle, you should see your doctor or vein specialist to stop the progression of venous insufficiency and prevent the skin from forming an ulceration.
Chronic venous insufficiency over time can lead to skin changes and eventually ulceration. This image demonstrates stasis dermatitis (also known as venous dermatitis). Stasis dermatitis refers to the skin changes including skin discoloration around the ankles, dry itchy skin that can be thin, and it may eventually break down to cause an ulceration. You need to see a doctor if these signs are present.
Eight symptoms to watch out for:
- Swelling around ankles
- Heavy legs
- Varicose Veins, which can be twisted, bulging, dark, or purple
- Itching
- Pain
- Sores that ooze, crust or become scaly
- Thickened skin around ankles or your shins
- Hair loss on ankles and shins